Rules of Inference in Artificial Intelligence
| Institution | Jomo Kenyatta University of Science and Technology |
| Course | Information Technol... |
| Year | 3rd Year |
| Semester | Unknown |
| Posted By | Jeff Odhiambo |
| File Type | |
| Pages | 7 Pages |
| File Size | 235.51 KB |
| Views | 1643 |
| Downloads | 0 |
| Price: |
Buy Now
|
Description
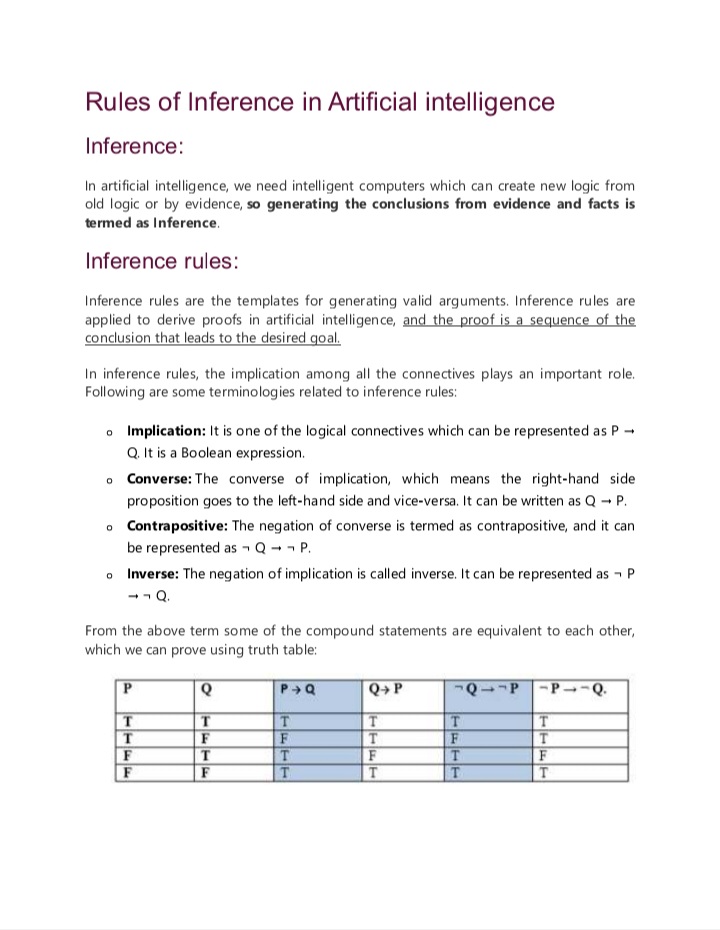
Rules of Inference in Artificial Intelligence (AI) are logical principles that enable the derivation of new truths from existing knowledge, ensuring sound reasoning in automated systems. They help AI systems in theorem proving, automated reasoning, and decision-making by systematically deriving conclusions from a given set of premises. Effective use of these inference rules enhances the ability of AI to reason, solve problems, and make logical decisions in knowledge-based systems.
Below is the document preview.
IO Device Management
Trending!
I/O (Input/Output) device management refers to the process of controlling and coordinating the operations of input and output devices within a computer system. This is typically handled by the operating system to ensure that data is transferred efficiently between the CPU, memory, and I/O devices.
3 Pages
2210 Views
0 Downloads
287.72 KB
Memory Management
Memory management refers to the process of efficiently allocating, organizing, and using computer memory in a system to ensure optimal performance and stability. It is a critical function of an operating system (OS) and is essential for executing programs and processing data.
6 Pages
1912 Views
0 Downloads
240.33 KB
Operating Systems Design and Implementation
Trending!
Systems Design refers to the process of defining the architecture, components, modules, interfaces, and data for a system to meet specified requirements. It is the blueprint for how the system will operate and interact with other systems or users. This phase follows the analysis phase in the systems development life cycle (SDLC).
Systems Implementation is the phase where the designed system is developed, tested, and deployed. It involves translating the plans into an operational system that meets user needs. Implementation often includes installation, configuration, training, and ongoing support.
1106 Pages
2035 Views
0 Downloads
21.97 MB
Operating System Exercise Questions
Trending!
Components of a thread which are not shared
Components of a thread which are shared
Benefits of threaded execution
Models of threads and for each explain advantages and disadvantages
2069 Views
0 Downloads
10.29 KB
ICS 2202: Internal and design Principles
Internal principles define the core components, structures, and processes that ensure an IT system operates efficiently, reliably, and securely.Design principles focus on creating systems that are usable, maintainable, and aligned with business needs.
3475 Pages
1941 Views
0 Downloads
31.24 MB
ICS 2202: Process Co-ordination
Trending!
When a process is being executed, the operating system must store information about a
process in a PCB. When scheduler switches CPU from executing one process to another, context
switcher saves the contents of all processor registers in process descriptor. That is, the context of
a process is represented in a PCB of a process.
5 Pages
2005 Views
0 Downloads
251.41 KB
ICS 2202: Process Management
Trending!
Process Management refers to the planning, monitoring, and controlling of activities involved in achieving specific goals or outputs within an organization or system. It ensures that processes are executed efficiently and effectively, using available resources while maintaining quality, consistency, and alignment with organizational objectives.
5 Pages
2016 Views
0 Downloads
248.85 KB
ICS 2202: Processor
A processor, also known as a central processing unit (CPU), is the primary component of a computer that performs most of the processing inside the system. It acts as the "brain" of the computer, interpreting and executing instructions from software programs.
2 Pages
1875 Views
0 Downloads
123.84 KB
ICS 2202: Protection and security
Protection and security are critical aspects of an operating system (OS) that ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data and system resources.
5 Pages
1896 Views
0 Downloads
173.71 KB